

This Research Topic aims to advance the understanding of (1) key processes in the major components of the hydrological cycle and associated atmospheric circulation and (2) how uncertainty accumulates in the cycle from the warming to changes in precipitation. For floods and droughts, the actual atmospheric water vapor amount obtained from the evaporation and transport needs to be compared with the water vapor holding capability, which is also affected by the warming. The atmospheric instability and general circulation driven by, e.g., the ENSO, should thus be focused from this specific perspective. Further understanding and investigations of hydrological cycle and atmospheric circulation entail: (1) examining the couplings between the warming and humidity as well as between the low-level atmospheric circulation and surface conditions and (2) identifying whether the atmosphere in the major condensation levels can gain more water vapor through vertical and horizontal motions. 1 Introduction Heavy precipitation, intense snow melting, and flooding are among the most significant hydrological extremes in the western United States, and they cause huge societal and economic losses every year (Barth et al., 2017 Cayan et al., 1999 Diffenbaugh et al., 2012 Kunkel et al., 1999 McCabe et al., 2007 ).
#CAUSES OF EARTHS ATMOSPHERIC AN HYDROLOGICAL PROCESSES HOW TO#
In this sense, the exigencies of how to bridge global warming and changes in precipitation have gained soaring attention. The resulting meridional overturning cells in the tropical atmosphere are called Hadley cells, or Hadley circulation.Floods and droughts tend to be severer and occur more frequently in the warming climate, whereas there are still too many uncertainties regarding projections of global and regional precipitation. exchanges of moisture and heat between the atmosphere Earths surface fundamentally affect the dynamics and t1Icnnodynamlcs of the climate system. Once the air returns to the equator it is saturated with water vapor (close to 100% relative humidity). hydrological cycJe influences climate in a variety of ways.

During this movement along the sea surface the air picks up water vapor from evaporation. The Coriolis force deflects it towards the right (left) in the northern (southern) hemisphere, creating the easterly trade winds in the tropics. Subsequently the dry air moves back towards the equator. This leads to dry conditions in the subtropics indicated by the major deserts at those latitudes. During the descend the air warms and its relative humidity decreases. This increases the density and the air descends back to the surface in the subtropics (~30°N/S). The air cools by emitting longwave radiation to space. As air rises into re- gions of lower pressure, it expands and cools, and that cooling causes water. Now the Coriolis effect kicks in, deflects the air towards the right (left) in the northern (southern) hemisphere, which creates the jet stream. The same process is essential for creating precipitation.
The cool relatively dry air then moves poleward. They can reach the top of the troposphere or higher. Some of the deepest cumulonimbus clouds on Earth form in the tropics.
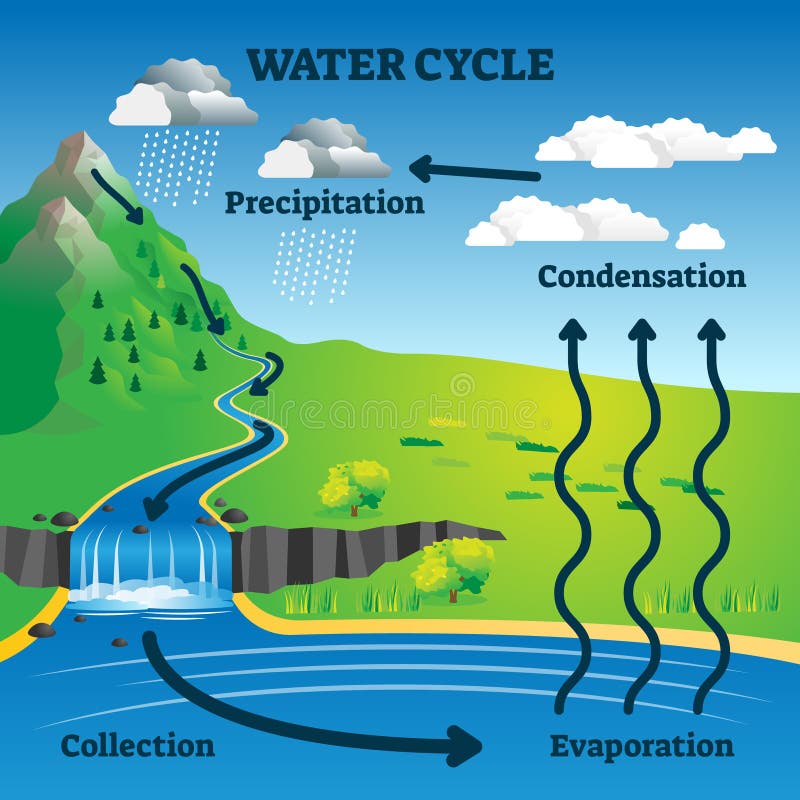
Rising of warm moist air at the equator causes water vapor condensation due to cooling of the air during the ascent. \): Atmospheric Circulation on a Rotating Earth.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
